California wildfires are on the rise. In just the first half of 2021, the Golden State experienced over 4,900 fires and lost over 142,000 acres of land. So what is the cause of California wildfires today than a decade ago, and how is it affecting the state? Let’s find out.
Main Factors Fueling California’s Wildfires

According to researchers and forestry and fire protection agencies, these are the factors fanning California’s flames:
1. Climate Change
Global warming has accelerated over the past decade, leading to rising temperatures and prolonged droughts in California. In 2020, Los Angeles County and neighboring areas recorded California’s highest temperature ever at 121 degrees Fahrenheit. In 2021, Death Valley surpassed that record with 130 degrees Fahrenheit on the thermometer.
As California gets hotter and drier, the foliage turns into tinder, and even the smallest spark can lead to several acres quickly going up in flames. According to the New York Times, nine of the 10 largest fires in California happened in the last decade. Records also show the hottest heatwave in California’s history over the last 10 years. The connection between these two factors cannot be clearer.
As climate change worsens and rains become more infrequent in the region, the frequency and ferocity of California fires will likely intensify. Even worse, due to the continued drought,
California’s fire seasons have lengthened by 75 days.
2. Rising Winds
Strong winds, combined with lots of dry foliage, make the perfect breeding ground for wildfires. The wind carries sparks, spreading flames to areas they would normally not reach. As the wind changes, so will the direction of the flames, making wildfires unpredictable and far more dangerous.
Certain parts of California experience high winds that are strong enough to whip up fire tornadoes. A fire tornado is similar to a regular tornado, but instead of a pillar of swirling wind and debris, it’s a swirling pillar of smoke and fire. These swirling flames can travel long distances, spreading burning ashes that trigger their own fires.
Besides fueling wildfires, high winds frustrate air support from planes and helicopters carrying water and flame retardant. According to a 2018 study, most massive fires in Southern California occur between June and September and October and April.
Fires from June to September spread with the help of warm and dry winds, whereas the October to April fire season benefits from the Santa Ana winds from the Great Basin and the Mojave Desert. According to the New York Times, the October to April winds are the worst, fueling fires to grow three times faster than usual and driving them toward populated areas.
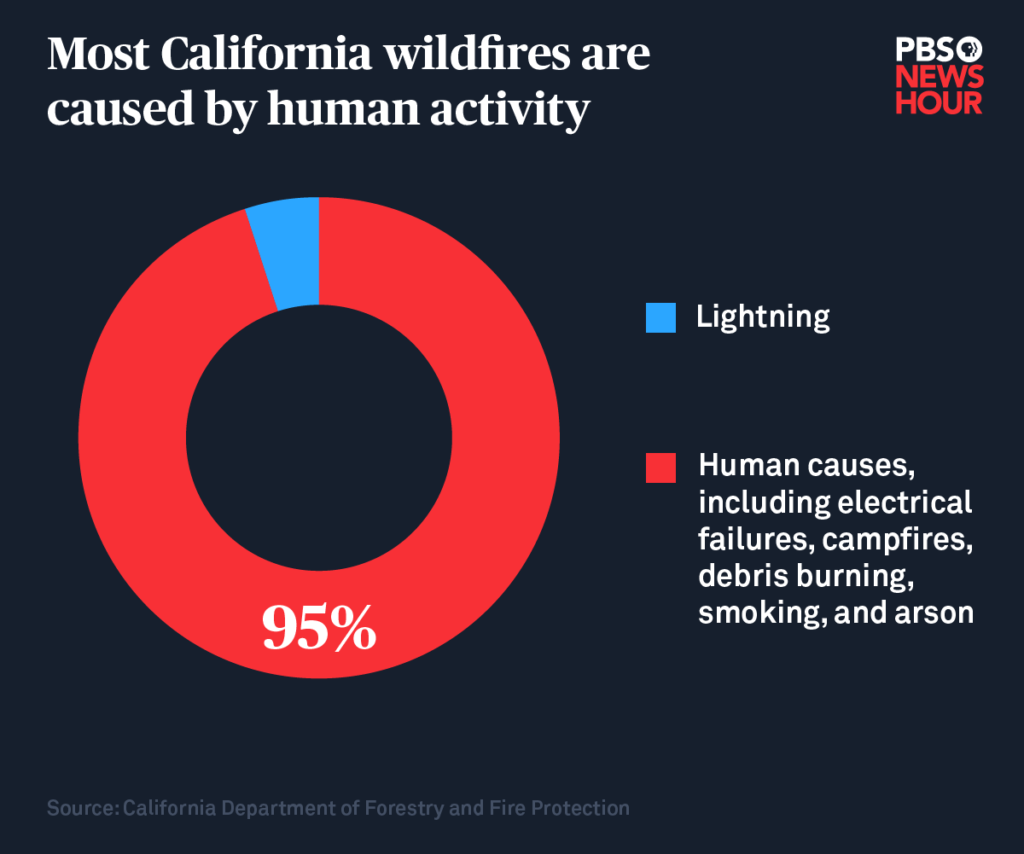
3. Humans
According to the Insurance Information Institute, people cause up to 90% of wildfires in the U.S. The fires may start due to human error or arson. Either way, the effects are expensive and deadly — Northern California fires in 2020 alone claimed 33 lives and destroyed over 10,400 structures.
In some instances, the fire comes from things that humans have put in place. For instance, power lines throw off sparks that land on dry vegetation and trigger wild infernos.
The Dangers of Wildfires Caused in California
Besides the obvious threat of burns and incinerating properties, wildfires pose several other dangers, such as:
- Soot and smoke damage: Smoke from fires can cling to the walls and roof of your building, ruining its curb appeal. Soot can also enter your building and damage your HVAC system and other appliances.
- Health threat: Inhaling carbon monoxide and particulate matter from fires poses several health risks. The risk of heart attack is higher in older adults who inhale such particulates, especially if they have underlying health issues. That’s why forestry and fire protection agencies recommend wearing dust masks when you notice airborne debris from wildfires.
During a wildfire, keeping smoke out of your premises will reduce the risk of long- or short-term damage to your health. If you have a central HVAC system, install high-efficiency filters, like HEPA filters that eliminate up to 99% of airborne particulates. If your home is in the path of the fire, evacuate safely and long before the flames reach your area.
Pursuing Compensation From Your Insurer For Property Damages Caused By Wildfires

If you live in a fire-prone part of California, your home insurance policy must cover fire and smoke damages to claim. Otherwise, the cost of recovering from property damage caused by a fire may be too much to bear. Should you need help filing a claim and pursuing compensation from your insurer, our California wildfire lawyers at Era Law, Inc., can help.
Reach out to us today to schedule a free case evaluation.
